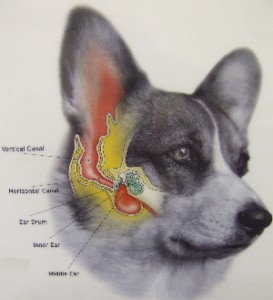
Dog ear infections are commonly seen in many breeds but why is this ?
Certain breeds such as those with long floppy ears may be more susceptible, but we do see ear infections in all breeds with all types of ears.
The main causes are
- Bacterial or fungal infection– if the ear becomes full of wax, it blocks the air flow into the ear, and it becomes hot and sticky. The normal bacteria or fungi that live on all skin can then grow rapidly and cause an infection. This often causes the ear to give off a pungent smell.
Treatment involves a visit to your vet to confirm the infection and then usually a course of antibiotic containing ear drops, possibly with an ear cleaner and oral antibiotic tablets.
Prevention- keeping the ear free from a build up of wax is the most important way to prevent ear infections. You can use an ear cleaner which helps dissolve and move the wax out of the ear once or twice weekly.
- Allergies– unfortunately allergies are common in dogs to a variety of indoor and outdoor allergens. The commonest allergen is the house dust mite, however other allergens such as pollens and grasses can occur. Food allergies are rarer but do sometimes occur. All of these allergens can cause inflammation and redness of the outer ear and ear canal lining. This causes increased secretion of wax and a secondary infection often follows.
Treatment involves investigation of underlying allergies with possibly exclusion diets, or blood tests. The allergy will need to be treated as well as the ear infection, to prevent recurrences of the ear infection.
- Ear mites can be the cause of an infection, but as they are passed on by close contact between dogs such as grooming each other, they are much more common in young puppies. If your puppy has noticeably waxy ears you should ask your vet to check him for ear mites.
Treatment may involve ear drops for some weeks and a spot on treatment such as stronghold.
- Grass seeds can lodge in the ear canal and cause acute onset head shaking as well as secondary ear infections. They are mainly a problem in the summer months.
Treatment usually requires either heavy sedation or anaesthetic to remove the grass seed as it often passes deep down to the level of the ear drum.